2021 outlook: portfolios need a broader mix as the pandemic prolongs the uncertainty

Summary
While investors can approach 2021 with optimism that an effective Covid-19 vaccine will be available, the path of the economic recovery remains unclear. A broader toolkit of investments is needed – not just the regions, sectors and strategies that have recently done well.
Key takeaways
|
2021 global outlook
While the worst of the recession is behind us, returning to the pre-coronavirus growth trajectory could take years
The global economy has recovered from the depths of the Covid-19 recession even as some countries grapple with new infections and lockdowns. Investors may want to seek out new sources of return potential that could benefit from the evolving recovery story – in addition to sectors that have prospered through the crisis.
Much depends on the successful deployment of an effective vaccine and drug therapies. New vaccines appear to hold promise, but we will be watching key macroeconomic data points for signs of momentum – and we expect wide differences in how regions perform. If the coronavirus is con-tained, attractive areas may include European and Asian equities, value sectors and corporate bonds. For institutional investors, private markets offer potential – infrastructure in particular could see increased spending, thanks in part to stimulus measures meant to boost economic activity. There are also an increasing number of opportunities to support a sustainable, resilient recovery of the post-coronavirus economy in ways that address climate change and other vital issues.
But if the pandemic is not brought under control, economic activity seems likely to reach pre-coronavirus levels only by the end of 2021. Economies might not return to their pre-coronavirus trend path for several years.

This uncertainty is reflected in the OECD’s unusually wide range of growth forecasts (see Exhibit 1), with scenarios for 2021 varying from 7% to -2%.
Countries have used stimulus to fight the coronavirus – but there may be economic casualties in the long term
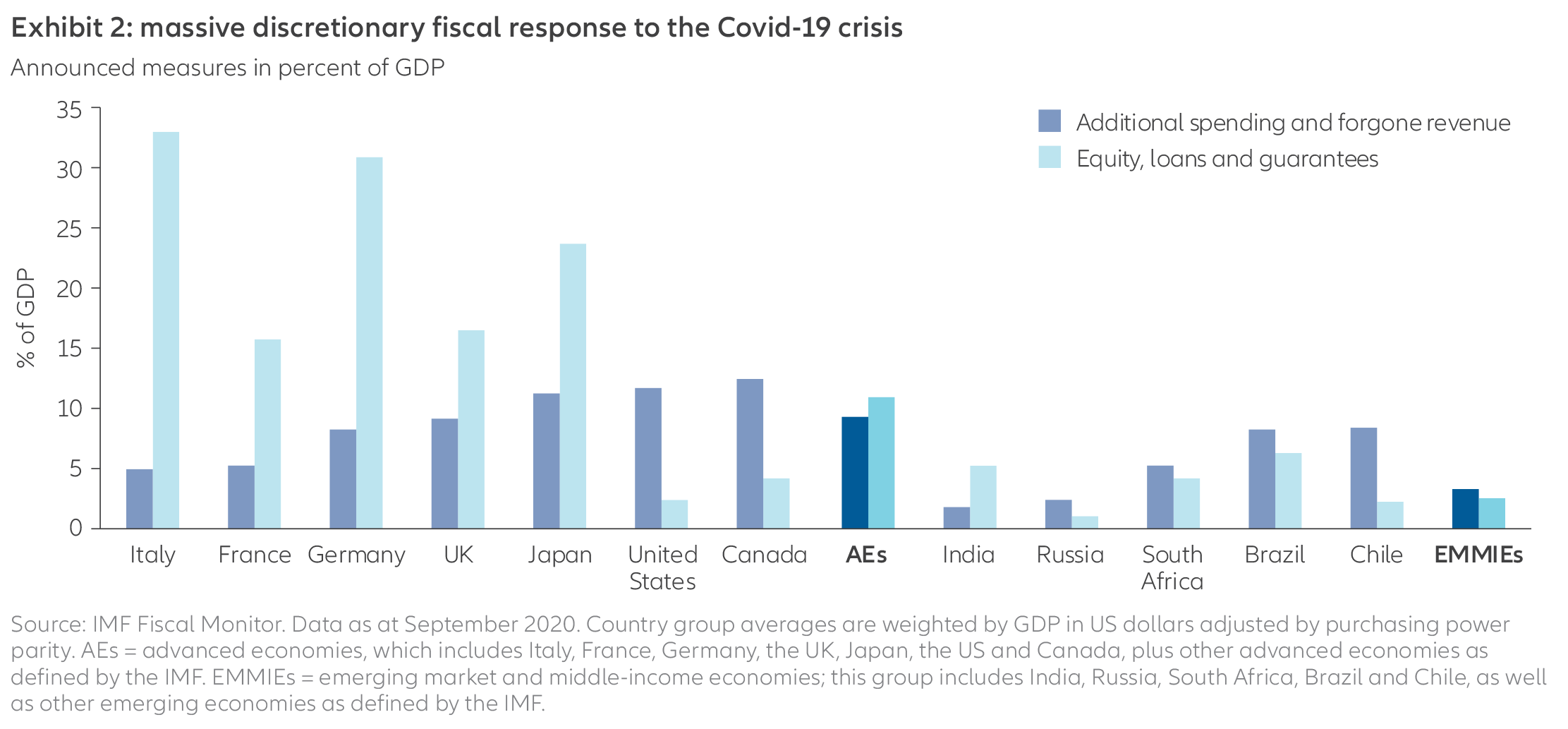
In response to the recent recession, governments and central banks provided vast amounts of monetary-policy stimulus and fiscal stimulus (see Exhibit 2). But although this support was necessary and helpful, it may also result in painful long-term side effects that include:
- High asset prices in some markets. Excess liquidity from monetary stimulus (essentially, too much money in circulation relative to economic activity) lifted asset prices – even some that already appeared overvalued. We think this is particularly true with government bonds and US equities, while non-US equities appear more moderately priced.
- High leverage. Public and private debt levels are elevated. If the recovery weakens significantly, companies might struggle to maintain their debt burdens – raising the risk of defaults. In addition, weak companies that renew cheap bank loans can turn into “zombie companies” – businesses with low productivity, high debt and a high risk of default if rates normalise.
- Rising inflation volatility. Risks are mounting that the prices for goods and services will grind higher in the medium term due in part to the excess liquidity from monetary stimulus, but also due to supply-side shocks related to the coronavirus shutdowns and ongoing trade wars. A continuation of the deglobalisation trend – as countries seek to be self-sufficient with essential goods – would be a drag on long-term economic growth and, consequently, on productivity growth. All else being equal, this could point to higher price volatility globally in the coming years.
Four investment themes to watch in 2021
1 Financial repression “reloaded” and massive government debt could drive up long-term yields
Given the support that central banks pledged in the face of Covid-19, we expect short-term interest rates to remain at ultra-low levels for the foreseeable future. This is essentially a “reloading” of the financial-repression policies (including low interest rates, restricted capital flows and other regulations) that central banks implemented after the financial crisis to help their economies grow their way out of debt. In our view, continued intervention by central banks is necessary, but it could still lead to higher inflation and other problems (as noted above) in the medium to longer term. In addition, a huge supply of sovereign bonds – the direct consequence of extremely expansionary fiscal policy – will continue to flood the bond markets in the coming quarters.
What does it mean for investors?
- All this supports our idea that the US yield curve in particular is likely to steepen – meaning that the difference in yields between longer-dated bonds and shorter-dated bonds would widen. (Bond prices and yields move in opposite directions.) While curve steepening could take place in various ways, we think the most likely scenario is that yields for long-dated bonds rise while those at the short end of the curve remain basically unchanged.
- Another argument in favour of curve steepening is that we don’t expect most major central banks to mirror what the Bank of Japan has done and implement yield-curve controls with bonds of different durations –targeting not just those on the shorter end of the curve, but also at the long end.
- Investors may want to consider inflation-linked bonds –including Treasury inflation-protected securities in the US and gilts in the UK. These should directly benefit from rising inflation expectations, since they are designed to help protect investors from inflation.
- Gold could also keep benefiting from easy monetary policy. There is a close historical connection between high gold prices and environments of low and falling real yields, because people often buy gold when they think other “safe” assets don’t offer a better opportunity.
2 Equities could benefit from positive news about the coronavirus – but balance and selection are key
Amid the upheaval of the Covid-19 pandemic and accompanying lockdowns, certain regions and asset classes did quite well – particularly US large-cap technology and online retail names that benefited from the “stay-at-home” trend. Positive developments in the fight against the coronavirus could help a broader range of stocks and regions in addition to these “coronavirus winners”.
One such positive development was the announcement of promising vaccine trials towards the end of 2020. Yet it remains unclear how long it will take to roll out these vaccines and how many people will be willing to get them. Until then, many regions will likely grapple with subsequent waves of coronavirus infections. So as we wait for effective vaccines and therapeutic treatments to be broadly adopted, the growth outlook will be unclear and private-sector spending (including private consumption and investments) could be suppressed.
If cyclical economic data lose momentum, equities could suffer – particularly if the markets see a disconnect between asset prices and the underlying health of the economy.
What does it mean for investors?
- Since there are still many unknowns for the markets, we suggest investors consider investing in a balanced equity portfolio rather than looking for a simple directional call that would indicate how to invest.
- For example, if the pandemic is really brought under control in 2021, we expect value cyclicals (such as industrials and financials) to outperform. But if Covid-19 remains a major threat, the winners of 2020 (such as the technology sector) could be the winners of 2021.
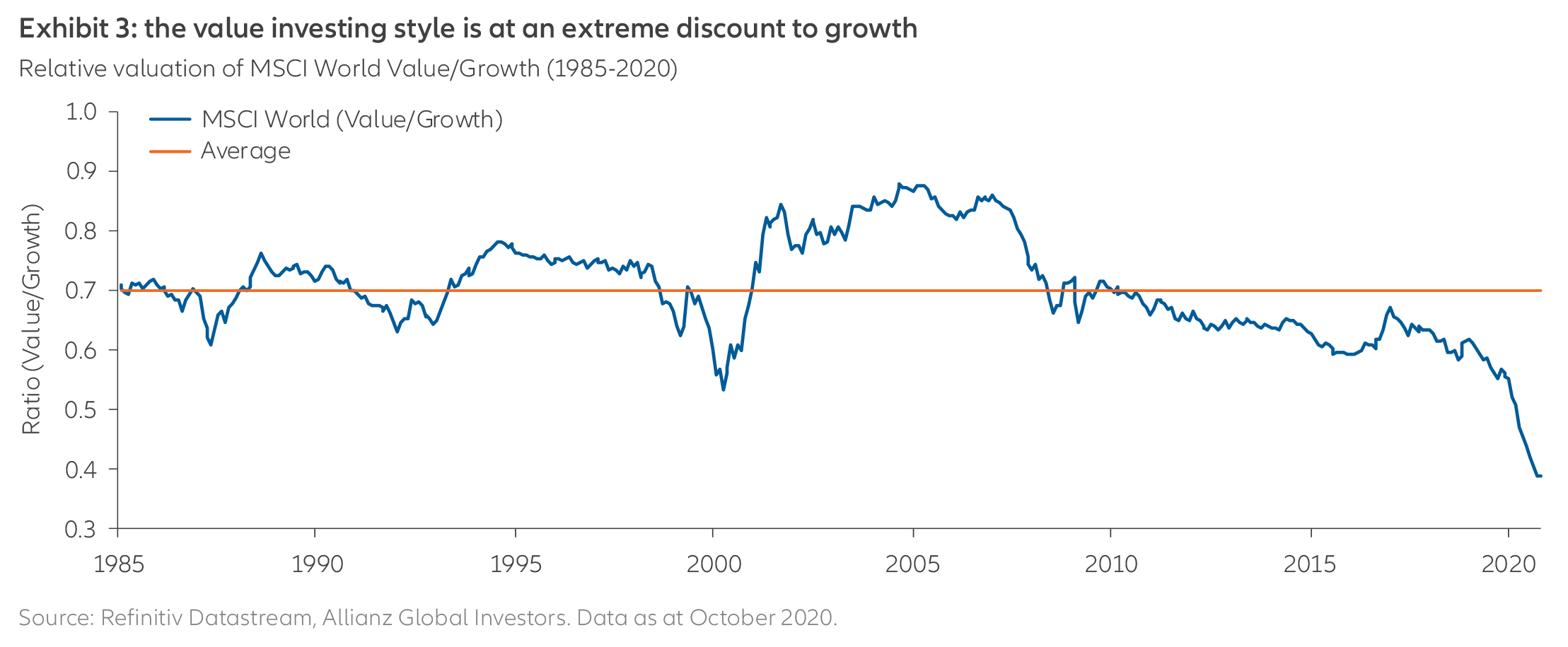
- Value stocks (which tend to have relatively lower valuations) could still have a positive outlook in 2021 compared with growth stocks (which tend to have higher valuations and revenue growth). As Exhibit 3 shows, value names are much cheaper than they have historically been. At the same time, it is too early to tell which way value stocks might go: we have not yet seen a catalyst that might cause the value/growth gap to close.
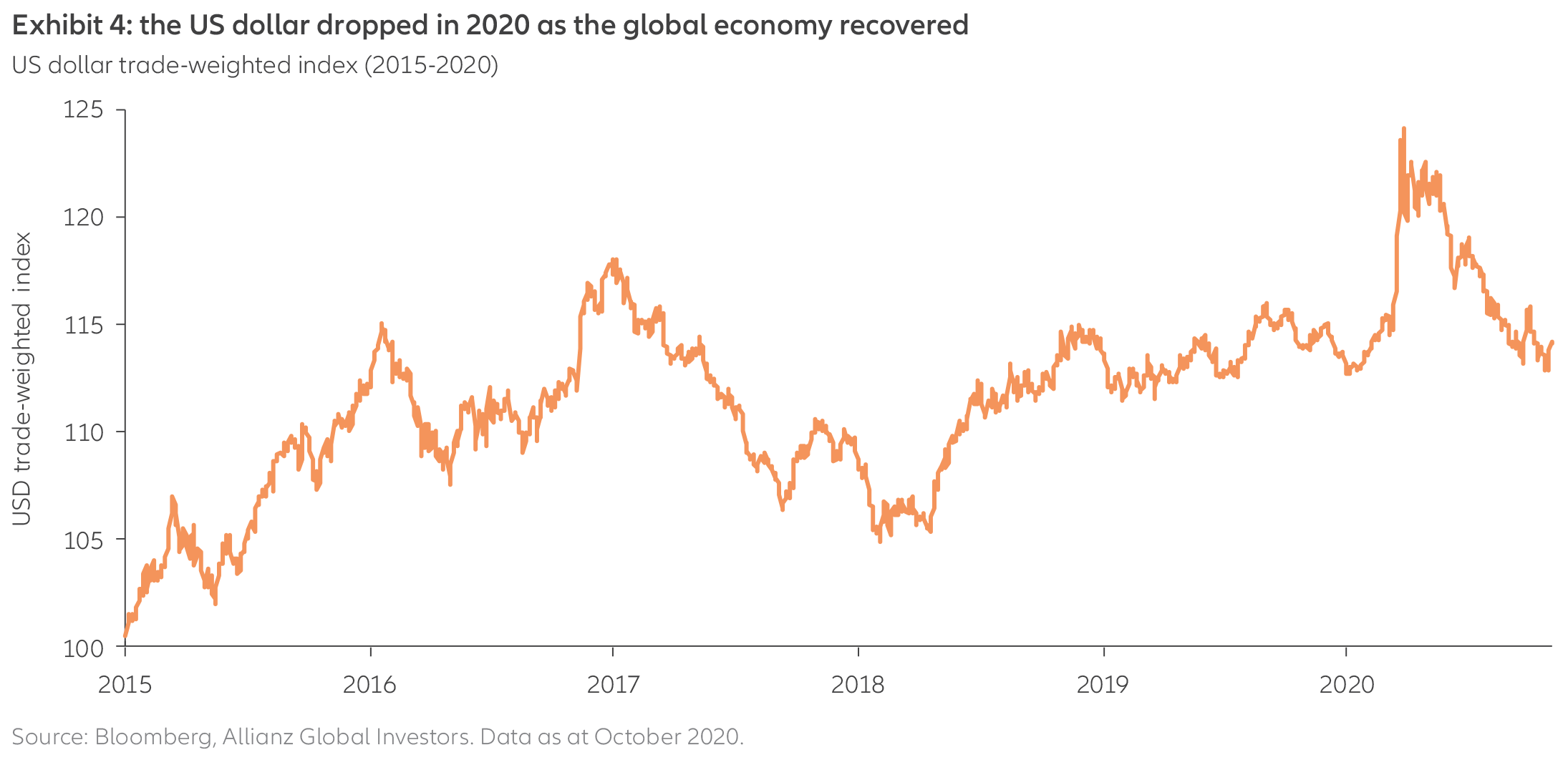
- Many growth themes are still attractive – particularly high-tech areas such as artificial intelligence and cyber-security. They represent longer-term secular changes that were already in place before the coronavirus. Think of them as deeper currents that investors may want to ride in addition to navigating the choppy waters on the surface.
3 The US dollar seems more likely to weaken, which would benefit non-US markets
As the global economic rebound ramped up, the US dollar fell in value relative to other currencies (see Exhibit 4). While some economists see a turnaround on the horizon – in large part because uncertainty about Covid-19 is supportive for “safe-haven” assets such as the US dollar – we are slightly more inclined to believe the dollar will fall for several reasons:
- The dollar is still historically overvalued.
- US monetary policy is “easing” more aggressively than non-US monetary policy (including the Federal Reserve moving towards targeting an average inflation rate). Easy monetary policy tends to weaken a country’s currency.
- There are no signs of US dollar funding stress – unlike what happened early in 2020, when companies and countries scrambled to obtain dollars.
What does it mean for investors?
- A weaker US dollar could be positive for certain large US companies that get much of their revenues overseas, since other countries would have additional buying power to purchase US goods.
- More likely, a weaker dollar indicates that the markets feel non-US economies have stronger prospects. This could be a good sign for non-US markets – particularly in Europe, which is undervalued compared with the US.
- Emerging-market equities that enjoy current-account surpluses – meaning they benefit from net exports – also tend to outperform developed-market equities during periods of US dollar weakness.
- Historically, when the US dollar has been weak, emerging-market credit spreads (their excess yields over similar US bonds) have grown smaller as the bonds rise in value. This could bode well for emerging-market debt in the coming year. We think investors should consider good-quality corporate bonds in Asia.
- A weaker US dollar could also spur inflation in the US,which could support our expectations for a steeper yield curve and make US Treasury inflation-protected securities more attractive.
4 Sustainable investing provides the long-term view investors need
The coronavirus pandemic exposed shared vulnerabilities in the global economy and the systems on which we all rely. Investors will increasingly need to find ways to be selective among sectors and individual names, rather than rely on broad market performance. Environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors can be a helpful lens for highlighting major global risks and testing the resilience of businesses and systems.
The Covid-19 pandemic also forced many investors to hit the “reset” button and recalibrate their priorities, with policymakers, regulators and investors examining the social effects of economic activity. A growing number of investors will want to put their capital to work in a sustainable way, and they’ll be looking for creative ideas to help achieve meaningful real-life change on topics such as climate change.
This may happen within the framework of the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which call for greater cooperation between countries, organisations, companies and individuals to address vital development issues. A 2017 UN report put the SDG funding gap in developing countries at around USD 2.5 trillion per year, making it critical to find innovative and scalable new investment products for the countries and sectors most deprived of funding. This can take the form of public/private partnerships, with parties with similar goals shouldering different responsibilities. The field of development finance – which uses capital and know-how from public and philanthropic sources to mobilise private investment into sustainable development – can play a crucial role here. For example, given that massive spending is still needed to return parts of the economy to its pre-pandemic growth trajectory, some governments see an opportunity to rejuvenate existing infrastructure such as electricity networks. This can be done while building the social, environmental and clean-energy projects that will support the well-being and prosperity of future generations.
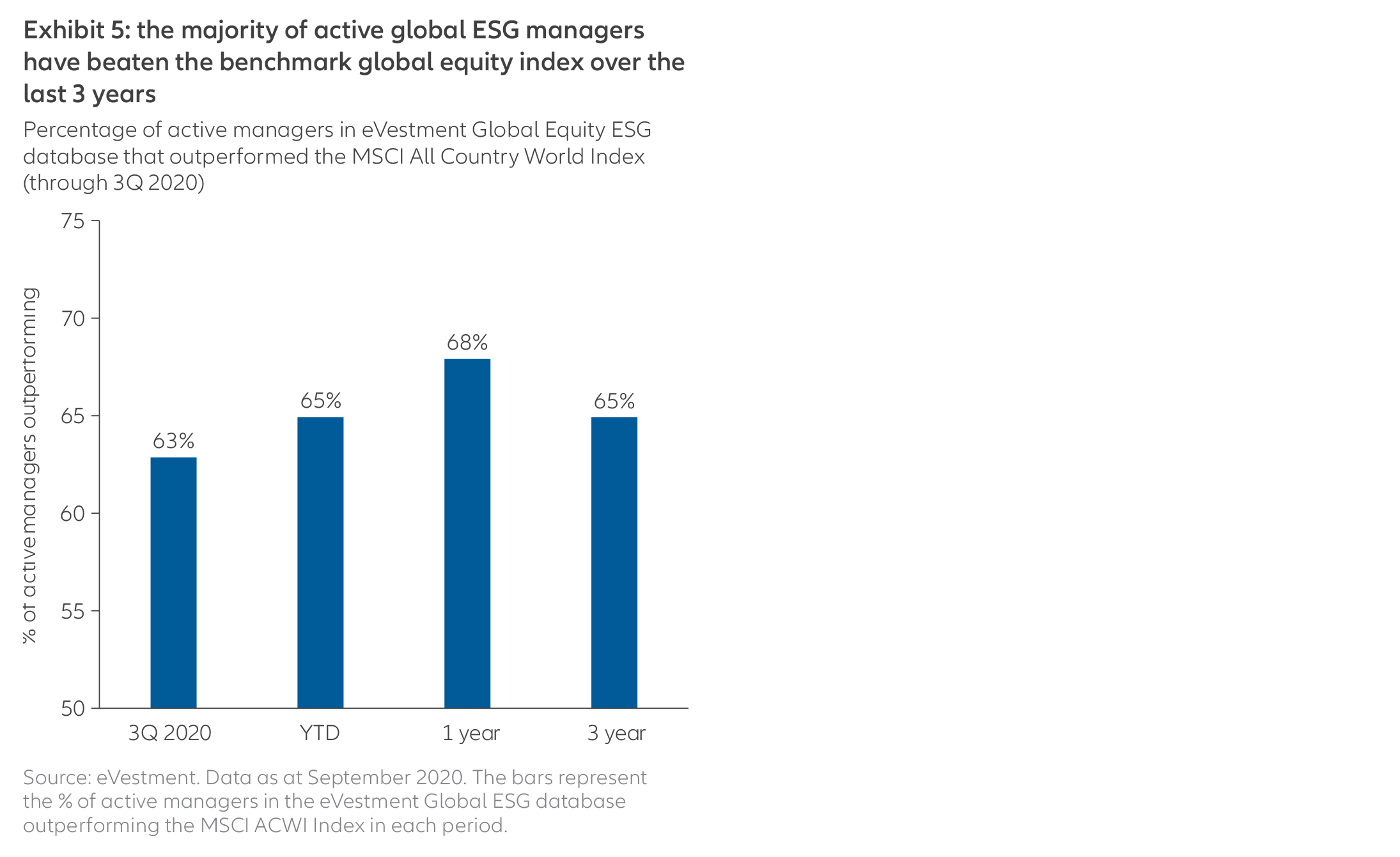
But sustainable investing is not just about doing good – it also helps investors seek solid performance. As Exhibit 5 shows, approximately two-thirds of active ESG managers in the eVestment database (which tracks institutional asset managers) have beaten the benchmark index for global equities during the last three years. This includes 2020 – an extremely volatile period for equities.
What does it mean for investors?
There are many options for investors who want to put their money to work in a sustainable way – particularly as the world recovers from the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Examine ESG factors. Corporate governance will be critical as the private sector navigates a deep recession; well-run companies with solid governance structures may be in a better position than their competitors.
- Tap private markets. Institutional investors can turn to the private markets to seek financial alpha while also meeting societal targets – for example, by investing in urban regeneration, enhanced digital infrastructure, social housing, or improved education and health services.
- Look for investments tied to SDG themes. Consider the area of food security, which has garnered more attention during the pandemic as the food-supply chain was disrupted and an unexpected number of people needed assistance. Companies are making promising developments in the way food is grown, processed and distributed – and they’re looking for much-needed capital from investors.
2021 outlook: regional views

Summary
Amid the ongoing global economic recovery, investors may need to use a broader toolkit – beyond the regions that have recently done well. Equities in Europe and emerging Asia may offer better value than the US winners of 2020, while a continued low-yield environment could create attractive opportunities in Asian debt and corporate bonds globally.





